|
||
|
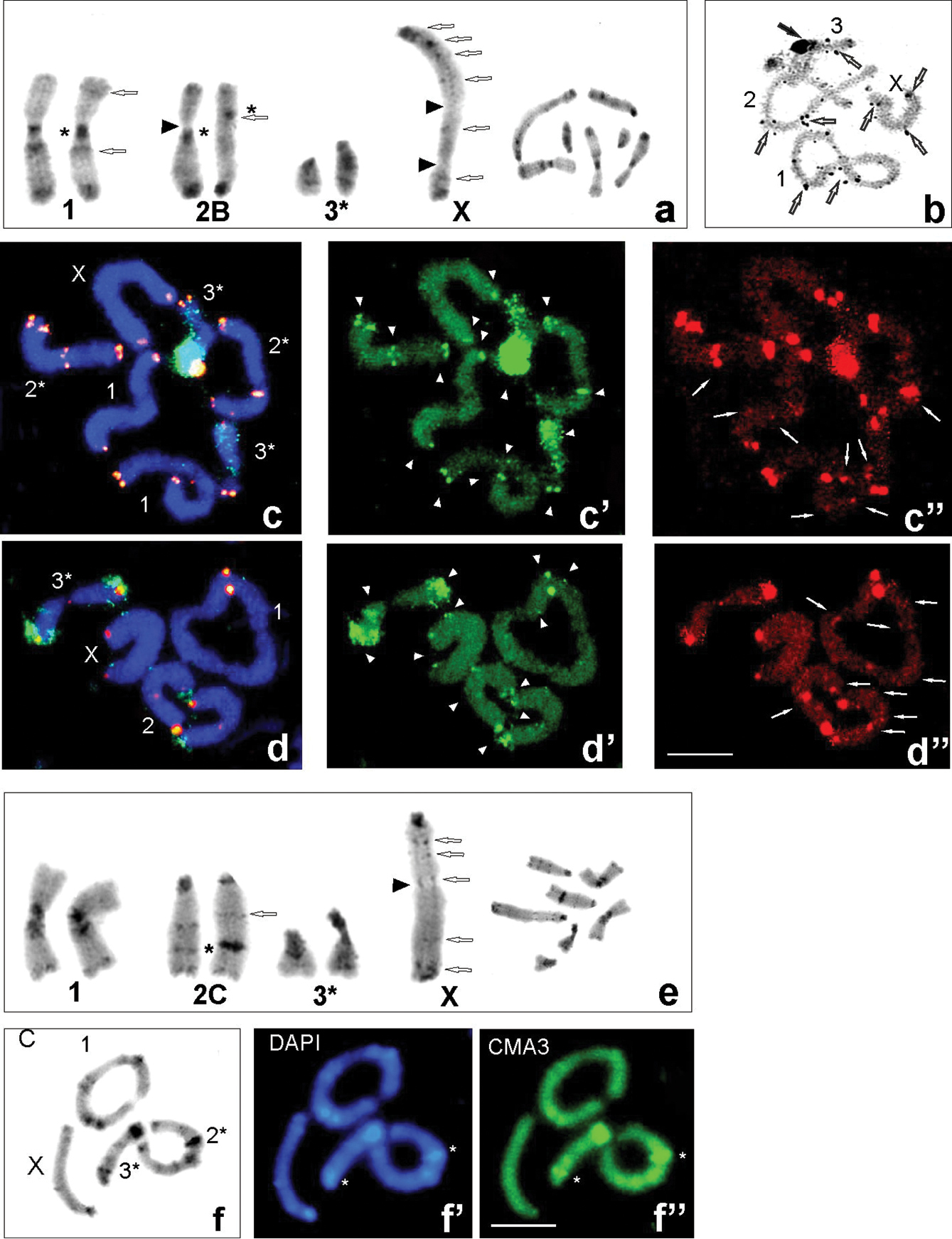
Examples of C-banding (a, e), silver nitrate staining (b), C-, DAPI and CMA3 stained heterochromatin (f–f”) and FISH (c–c”, d–d”) in individuals with karyomorph 2B (a–d”) and 2C (e, f”) from populations: Udzungwa Mts (Ud CH7949 and CH8088) (a, b), Ud CH8088 (c–c”), Uluguru Mts (Ul HE89) (d–d”). C-banding karyotypes of males chromosome complement (arranged from mitotic metaphase – right side); open arrows point to interstitial C-bands in the X chromosome and chromosome pairs 1st and 2nd; black arrowheads indicate secondary constriction (a, e). AgNO3 staining (b) at diplotene revealed large active NOR of the 3rd bivalent (black arrows) and very small NORs seen in the X and bivalents (open arrows). FISH using 18S rDNA (green – c, c’, d, d’) and telomeric DNA (red – c, c”, d, d”) probes in mitotic metaphase (c) and diakinesis (d); white arrowheads point to rDNA clusters near centromeric, interstitial and telomeric regions of the chromosomes (c’, d’) and white arrows ITS signals (c”, d”). C/DAPI/CMA3 blocks were located very close to each other, but bright CMA3 signals coincided with active NORs. Heterochromatin (a, e, f) and hybridization areas (c, d) vary in size between homologous chromosomes, which are marked with asterisks (*). The X chromosome is indicated. Scale bars: 10 µm. |